Which areas of the UK are at risk from pest or pathogen species?
Louise Barwell, Daniel Chapman and Bethan Purse
Environmental risk factors for establishment
The environmental tolerances of pathogens and pests can be estimated by matching patterns in their known occurrence with environmental and socio-economic variables like climate and land-use. The maps presented below can be used to explore the predicted suitability of 10km cells across the UK for nine Phytophthora species. The predictions are based on estimating how species global occurrences (excluding occurrences in the UK) are related to soil moisture, minimum Winter temperature, mean Summer temperature and land-use (agricultural, forest and urban cover).
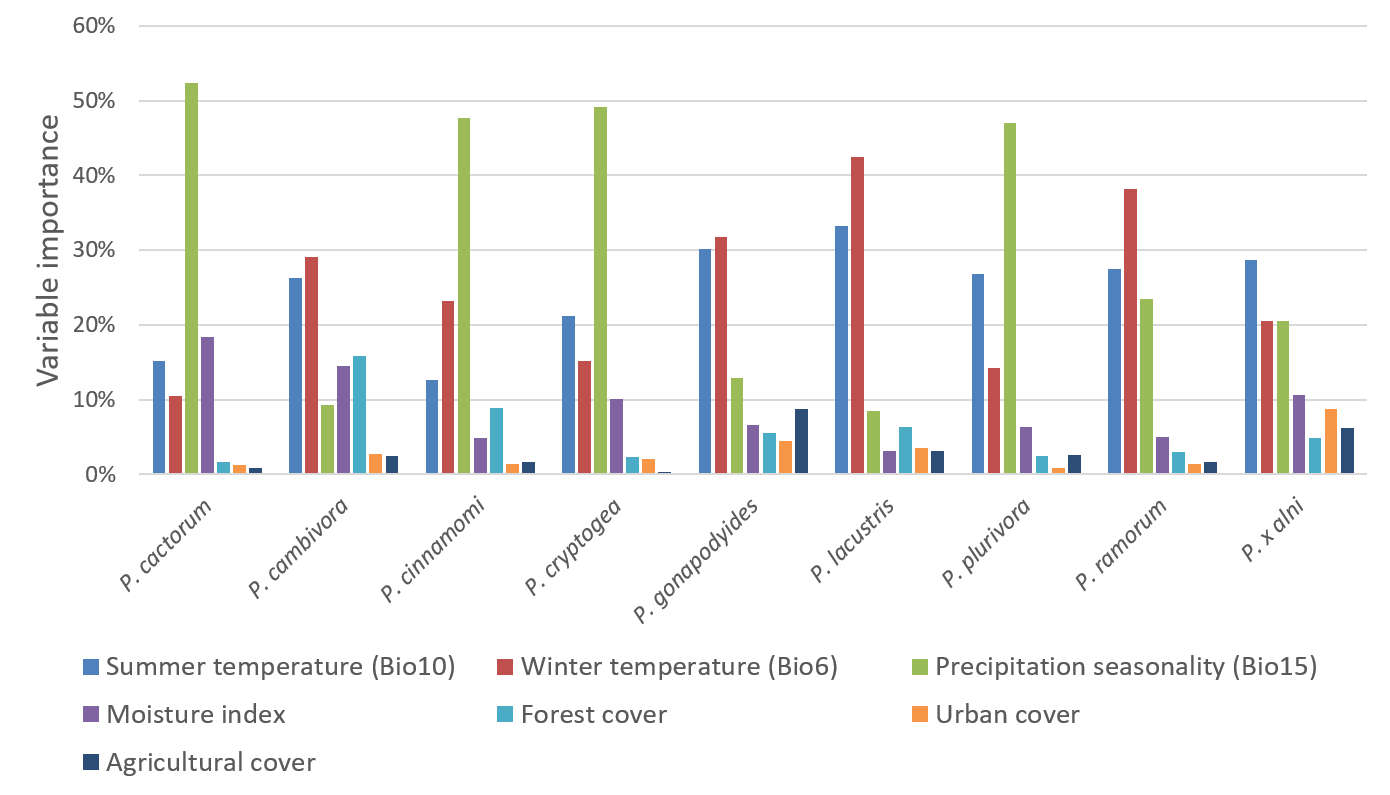
These relationships were then used to predict suitability across the UK for these species and to validate the predictions by comparing them to available records for each species. This was intended to provide proof-of-concept for whether these approaches could be used to predict the suitbility of the UK climate for Phytophthora pathogens that have not yet arrived in the UK.
These models were developed as part of the PHYTO-THREATS project: Global threats from Phytophthora species (https://www.forestresearch.gov.uk/research/global-threats-from-phytophthora-spp/). The study was supported by a grant funded jointly by the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council, the Department for Environment, Food and Rural affairs, the Economic and Social Research Council, the Forestry Commission, the Natural Environment Research Council and the Scottish Government, under the Tree Health and Plant Biosecurity Initiative (project reference BB/N023463/1).
Data sources
Information on Phytophthora outbreaks in the wider environment within the UK were provided by the Animal and Plant Health Agency, Science and Advice for Scottish Agriculture, the Royal Horticultural Society, Forest Research, Forestry Commission Scotland and Natural Resources Wales. They have been coarsened to 10km resolution to avoid identification of specific premises. No data from nurseries is presented.
Global Phytophthora distribution data were compiled from the literature and include contributed data from more than 100 expert pathologists.